Mediterranean Diet Higher Protein Vegetables List
- Maya Oueichek, MBA, RDN
- Aug 14, 2025
- 3 min read
This list spotlights Mediterranean Diet–friendly vegetables (excluding legumes) that can help you reach your protein goals per meal.
When you think of protein, vegetables might not be the first thing that comes to mind, but many veggies contain more than you’d expect.
From artichokes and spinach to broccoli, mushrooms, and even potatoes, these vegetables offer plant-based protein alongside fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants.
They’re a delicious way to boost your plate’s protein and nutrition while keeping meals colorful and plant-forward.
Save this as inspiration for building balanced, vegetable-rich meals.

Why Protein and Fiber Work Better Together
Protein helps you stay satisfied, maintain lean muscle, and keep energy steady. Fiber slows digestion, supports gut health, and helps regulate blood sugar. Together, they:
Improve satiety between meals
Support healthy weight management
Nourish your microbiome
Provide steady energy without crashes
This is why the Mediterranean Diet emphasizes whole foods that deliver legumes, leafy greens, starchy vegetables, and nuts.
Mediterranean Diet Higher Protein Vegetables List
1. Green Peas
Protein: 9g per cup
Other Benefits: Contains fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, and antioxidants; supports immunity and bone health.
Simple Use: Add to pastas, rice dishes, or soups for a pop of color and protein.

2. Spinach
Protein: 5g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: High in iron, magnesium, folate, and vitamin K; supports heart and bone health.
Simple Use: Sauté with garlic and olive oil, add to smoothies, omelets, or toss in salads.

3. Kale
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: Loaded with vitamin C, K, calcium, and antioxidants; supports anti-inflammatory and heart health.
Simple Use: Massage into salads, sauté as a side, or add to soups.

4. Broccoli
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: High in fiber, vitamin C, folate, and sulforaphane; supports detoxification and heart health.
Simple Use: Steam, roast, or add to stir-fries and grain bowls. You can also snack on them raw with hummus.

5. Brussels Sprouts
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: High in fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, and antioxidants; supports digestion and immune function.
Simple Use: Roast with olive oil and garlic or sauté. You can also shred them into salads and slaws.

6. Asparagus
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: Rich in folate, vitamins A, C, K, and antioxidants; supports heart and kidney health.
Simple Use: Grill, roast, or add to salads and pasta dishes.

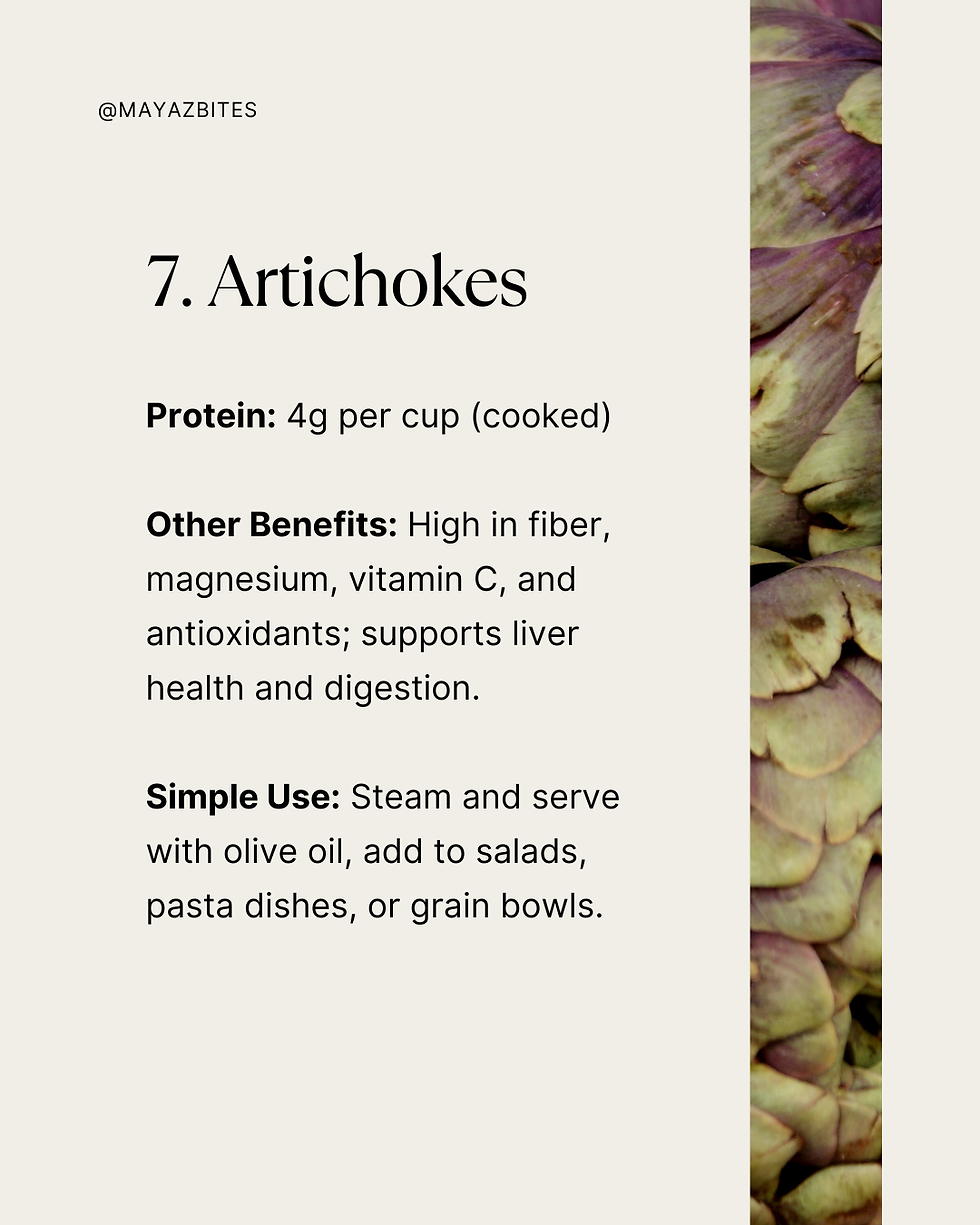
7. Artichokes
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: High in fiber, magnesium, vitamin C, and antioxidants; supports liver health and digestion.
Simple Use: Steam and serve with olive oil, add to salads, pasta dishes, or grain bowls.
8. Potatoes
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: High in potassium, vitamin C, and fiber (with skin).
Simple Use: Roast with olive oil and herbs, mash as a side, or cube for grain bowls.

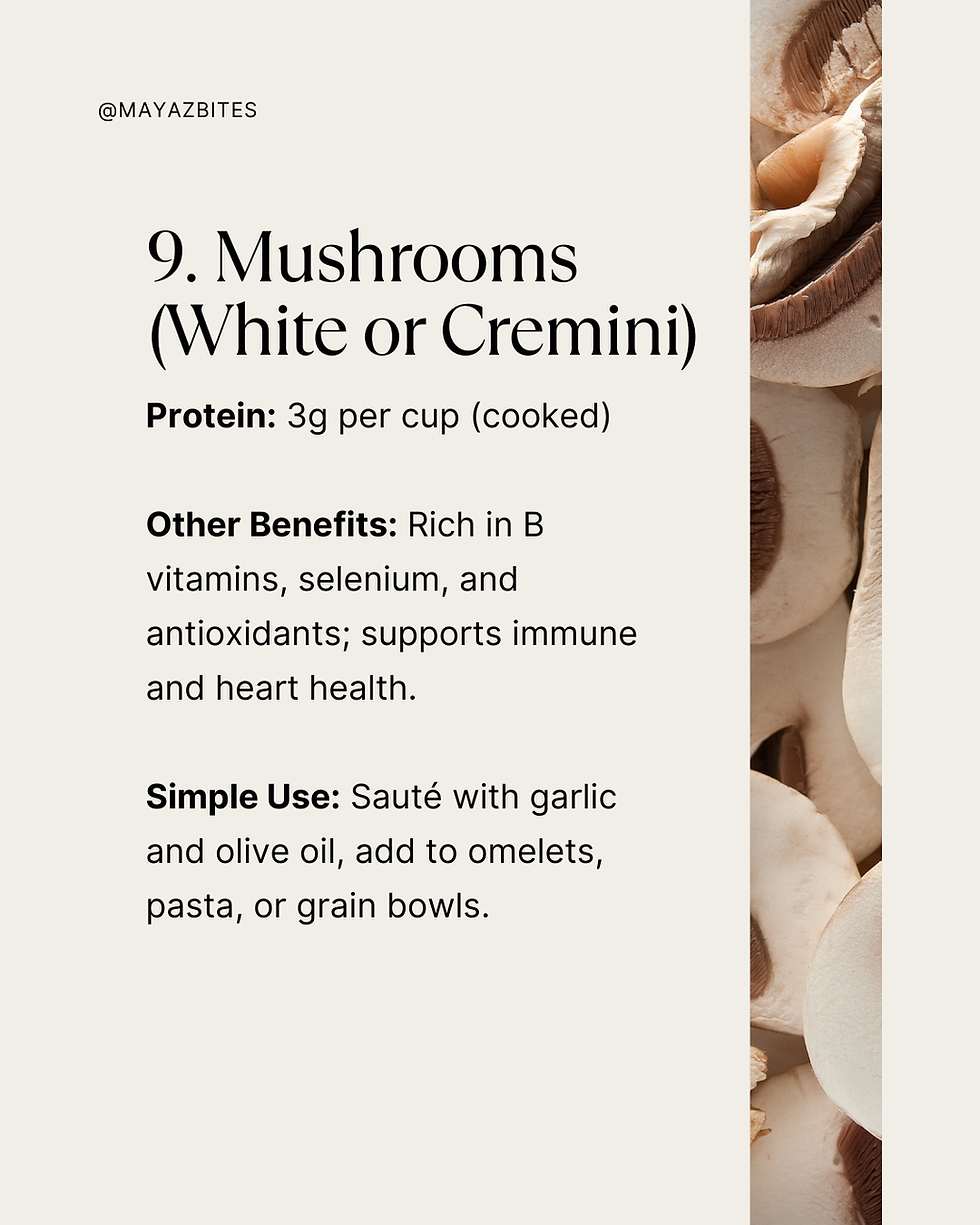
9. Mushrooms
(White or Cremini)
Protein: 3g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: Rich in B vitamins, selenium, and antioxidants; supports immune and heart health.
Simple Use: Sauté with garlic and olive oil, add to omelets, pasta, or grain bowls.
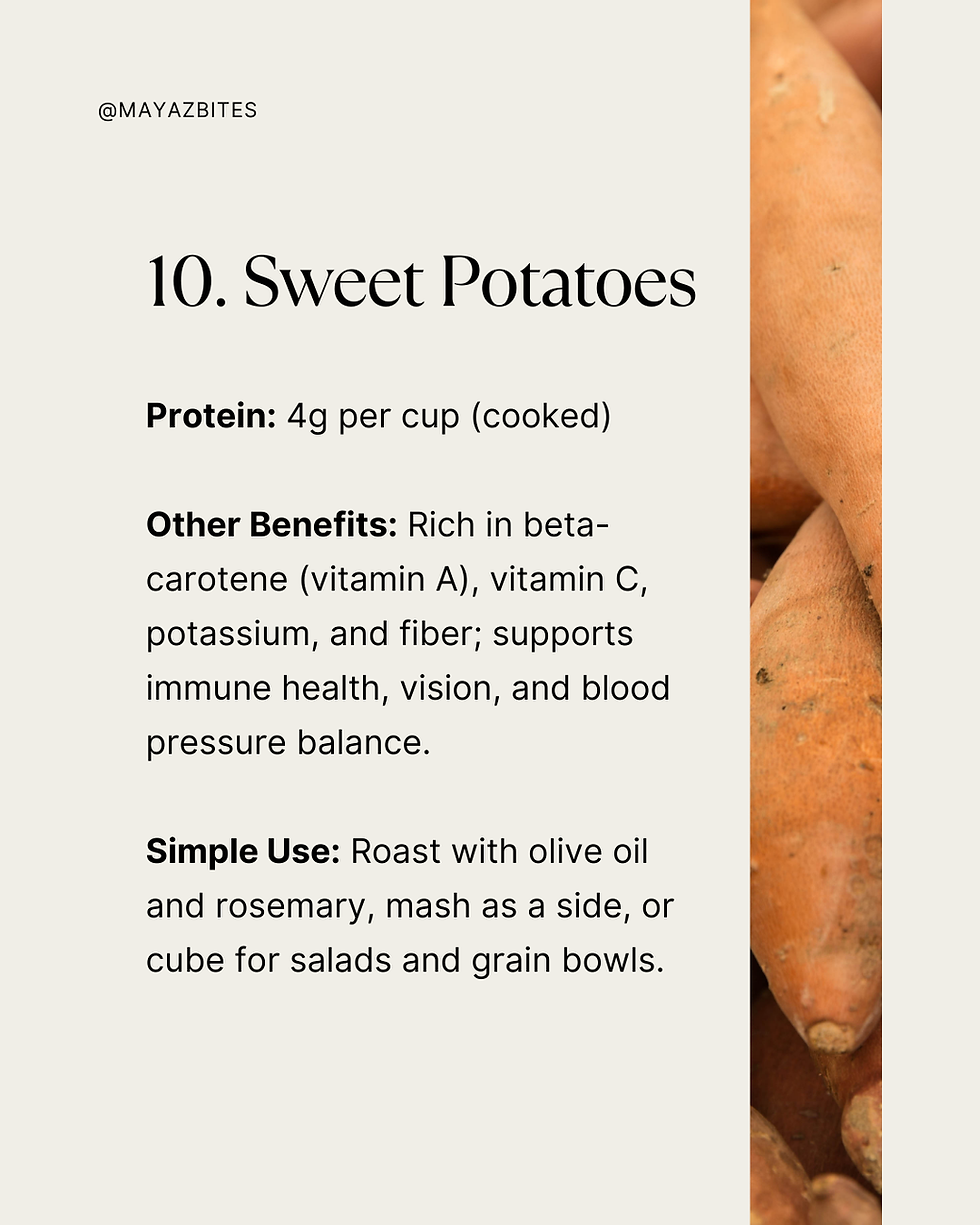
10. Sweet Potatoes
Protein: 4g per cup (cooked)
Other Benefits: Rich in beta-carotene (vitamin A), vitamin C, potassium, and fiber; supports immune health, vision, and blood pressure balance.
Simple Use: Roast with olive oil and rosemary, mash as a side, or cube for salads and grain bowls.
How Much Protein Should You Get Per Meal?
Most adults benefit from 25–30g of protein per meal, depending on activity level and health goals. Using higher-protein vegetables as part of your meal — alongside fish, poultry, or plant proteins — makes it easier to reach that range while keeping meals plant-forward.
You Might Also Like:
🧠 How to Build a Balanced Mediterranean Diet Meal?
Here’s a quick framework to follow:
Protein (¼ of your plate)
Choose fish (like salmon), chicken, legumes, or eggs to support satiety and muscle maintenance.
Fiber-rich veggies (½ of your plate)
Go for leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, zucchini — raw or roasted.
Healthy fats (a small handful)
Think olives, nuts, seeds, extra virgin olive oil, or avocado.
Complex carbs (optional, depending on hunger)
Whole grains like farro, quinoa, or barley, or a slice of sourdough bread on the side.
Flavor with purpose
Use herbs, spices, citrus, vinegar, and fermented ingredients to elevate taste without added sugars.

Mediterranean Diet Meal Plans:
Mediterranean Diet Shopping List:
Explore More: Mediterranean Diet Food Lists (Volumes 1–5)
Looking to build your Mediterranean pantry or refresh your grocery list? Browse these dietitian-approved food lists to discover what to stock up on.
Each list contains a selection of 10 items, including nutrition benefits highlights and simple ways to use.
Want More Mediterranean Diet Resources and Recipes?
Looking for more support on your healthy eating journey? Bookmark this post and explore others for comprehensive Mediterranean Diet resources and expert advice. Don't forget to check my social media and follow @Mayazbites






























Comments